Underage Drinking
Underage drinking is a serious public health problem in the United States. Alcohol is the most widely used substance of abuse among America’s youth, and drinking by young people poses enormous health and safety risks.
The consequences of underage drinking can affect everyone— regardless of age or drinking status. We all feel the effects of the aggressive behavior, property damage, injuries, violence, and deaths that can result from underage drinking. This is not simply a problem for some families—it is a nationwide concern.
Underage Drinking Statistics
Many, many young people drink alcohol
- By age 15, about 35 percent of teens have had at least 1 drink.1
- By age 18, about 65 percent of teens have had at least 1 drink.1
- In 2014, 8.7 million young people ages 12–20 reported that they drank alcohol beyond “just a few sips” in the past month.2
Youth ages 12 to 20 often binge drink
People ages 12 through 20 drink 11 percent of all alcohol consumed in the United States.3 Although youth drink less often than adults do, when they do drink, they drink more. That is because young people consume more than 90 percent of their alcohol by binge drinking. Binge drinking is consuming many drinks on an occasion (see box). Drinking alcohol and binge drinking become more prevalent as young people get older.
- 5.3 million young people had 5 or more drinks on the same occasion, within a few hours, at least once in the past month.4
- 1.3 million young people had 5 or more drinks on the same occasion on 5 or more days over the past month.4
More adolescents use alcohol than cigarettes or marijuana
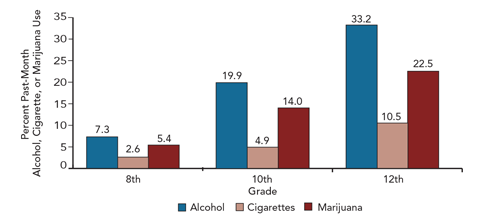

SOURCE: Johnston, L.D.; Miech, R.A.; O’Malley, P.M.; et al. Monitoring the Future National Survey: Trends in 30-Day Prevalence of Use of Various Drugs in Grades 8, 10, and 12, 2015. Ann Arbor, MI: Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan, 2015. Available at: http://www.monitoringthefuture.org/data/15data/15drtbl3.pdf. Accessed 01/06/2016.
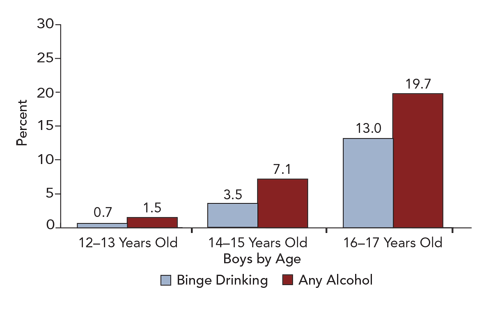
Drinking patterns vary by age and gender
As adolescents get older, they tend to drink more. Prevalence of drinking by boys and girls is similar, although among older adolescents, boys binge more than girls.
Alcohol use among boys

Alcohol use among girls
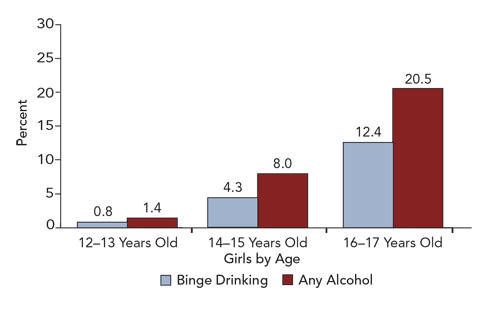

SOURCE: Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. 2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health Public Use File. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Underage Drinking Is Dangerous
Underage drinking poses a range of risks and negative consequences. It is dangerous because it:
Causes many deaths
Based on data from 2006–2010, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that, on average, alcohol is a factor in the deaths of 4,358 young people under age 21 each year.5 This includes:
- 1,580 deaths from motor vehicle crashes
- 1,269 from homicides
- 245 from alcohol poisoning, falls, burns, and drowning
- 492 from suicides
Causes many injuries
Drinking alcohol can cause kids to have accidents and get hurt. In 2011 alone, about 188,000 people under age 21 visited an emergency room for alcohol-related injuries.6
Impairs judgment
Drinking can lead to poor decisions about engaging in risky behavior, including drinking and driving, sexual activity (such as unprotected sex), and aggressive or violent behavior.
Increases the risk of physical and sexual assault
Underage youth who drink are more likely to carry out or be the victim of a physical or sexual assault after drinking than others their age who do not drink.
Can lead to other problems
Drinking may cause youth to have trouble in school or with the law. Drinking alcohol also is associated with the use of other drugs.
Increases the risk of alcohol problems later in life
Research shows that people who start drinking before the age of 15 are 4 times more likely to meet the criteria for alcohol dependence at some point in their lives.
Interferes with brain development
Research shows that young people’s brains keep developing well into their 20s. Alcohol can alter this development, potentially affecting both brain structure and function. This may cause cognitive or learning problems and/or make the brain more prone to alcohol dependence. This is especially a risk when people start drinking young and drink heavily.
Why Do So Many Young People Drink?
As children mature, it is natural for them to assert their independence, seek new challenges, and try taking risks. Underage drinking is a risk that attracts many developing adolescents and teens. Many want to try alcohol, but often do not fully recognize its effects on their health and behavior. Other reasons young people drink alcohol include:
- Peer pressure
- Increased independence, or desire for it
- Stress
In addition, many youth have easy access to alcohol. A 2013 study showed that 93.7 percent of adolescents ages 12–14 who drank alcohol got it for free the last time they drank.7 In many cases, adolescents have access to alcohol through family members, or find it at home.
Preventing Underage Drinking
Preventing underage drinking is a complex challenge. Any successful approach must consider many factors, including:
- Genetics
- Personality
- Rate of maturation and development
- Level of risk
- Social factors
- Environmental factors
Several key approaches have been found to be successful. They are:8
Environmental interventions
This approach makes alcohol harder to get—for example, by raising the price of alcohol and keeping the minimum drinking age at 21. Enacting zero-tolerance laws that outlaw driving after any amount of drinking for people under 21 also can help prevent problems.
Individual-level interventions
This approach seeks to change the way young people think about alcohol, so they are better able to resist pressures to drink.
School-based interventions
These are programs that provide students with the knowledge, skills, motivation, and opportunities they need to remain alcohol free.
Family-based interventions
These are efforts to empower parents to set and enforce clear rules against drinking, as well as improve communication between children and parents about alcohol.
The Role Parents Play
Parents and teachers can play a big role in shaping young people’s attitudes toward drinking. Parents in particular can have either a positive or negative influence.
Parents can help their children avoid alcohol problems by:
- Talking about the dangers of drinking
- Drinking responsibly, if they choose to drink
- Serving as positive role models in general
- Not making alcohol available
- Getting to know their children’s friends
- Having regular conversations about life in general
- Connecting with other parents about sending clear messages about the importance of not drinking alcohol
- Supervising all parties to make sure there is no alcohol
- Encouraging kids to participate in healthy and fun activities that do not involve alcohol
Research shows that children whose parents are actively involved in their lives are less likely to drink alcohol.
On the other hand, research shows that a child with a parent who binge drinks is much more likely to binge drink than a child whose parents do not binge drink.
Warning Signs of Underage Drinking
Adolescence is a time of change and growth, including behavior changes. These changes usually are a normal part of growing up but sometimes can point to an alcohol problem. Parents and teachers should pay close attention to the following warning signs that may indicate underage drinking:
- Changes in mood, including anger and irritability
- Academic and/or behavioral problems in school
- Rebelliousness
- Changing groups of friends
- Low energy level
- Less interest in activities and/or care in appearance
- Finding alcohol among a young person’s things
- Smelling alcohol on a young person’s breath
- Problems concentrating and/or remembering
- Slurred speech
- Coordination problems
Treating Underage Drinking Problems
Some young people can experience serious problems as a result of drinking, including alcohol use disorder. These problems require intervention by trained professionals. Professional treatment options include:
- Seeing a counselor, psychologist, psychiatrist, or other trained professional
- Participating in outpatient or inpatient treatment at a substance abuse treatment facility or other licensed program
For more information, please visit: www.niaaa.nih.gov.
1 National Survey on Drug and Alcohol Use (NSDUH) 2014. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUH-DetTabs2014/NSDUH-D…
2 National Survey on Drug and Alcohol Use (NSDUH) 2014. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUH-DetTabs2014/NSDUH-D…
3 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Fact Sheets: Underage Drinking. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/underage-drinking.htm
4 National Survey on Drug and Alcohol Use (NSDUH) 2014. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUH-DetTabs2014/NSDUH-D…
5 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Alcohol and Public Health: Alcohol-Related Disease Impact (ARDI). Available at: http://nccd.cdc.gov/dph_ardi/Default/Report.aspx?T=AAM&P=f6d7eda7-036e-4…
6 Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. The DAWN Report: Highlights of the 2014 Drug Abuse Warning Network (DAWN) Findings on Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits. Rockville, MD: SAMHSA, 2014. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/spot143-underage-drinking…
7 National Survey on Drug and Alcohol Use (NSDUH) 2013. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUHresultsPDFWHTML2013/… (See Section 3.2)
8 National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). Underage drinking: Why do adolescents drink, what are the risks, and how can underage drinking be prevented? Alcohol Alert, No. 67. Rockville, MD: NIAAA, January 2006. Available at: http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/AA67/AA67.htm.
Source:
https://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/UnderageDrinking/UnderageFact.htm

Recent Comments