by | | Research
The longer someone stays awake, the more likely they’ll start to nod off as their brain needs sleep. But how the brain senses that need for sleep hasn’t always been clear. Now, neurologists like Mark Wu, are investigating how this brain function works. He and his...
by | | Research
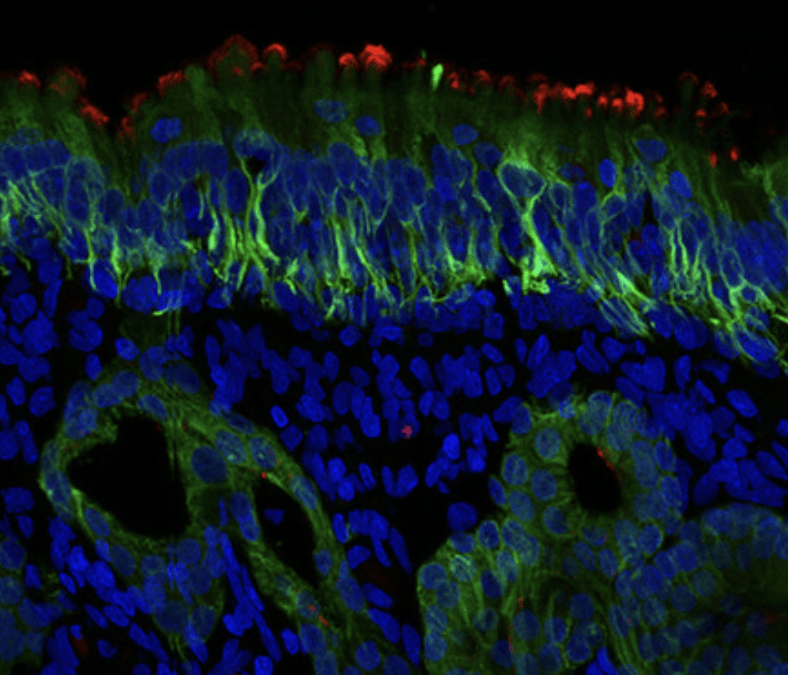
Why do people with COVID-19 lose their sense of smell? Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers believe it could be because the virus first enters through the cells in our noses. The researchers found that the cells that allow our sense of smell to function carry up to...
by | | Research
There is a protective coating around our nerve cells that helps our central nervous system send messages swiftly across our bodies. This insulation, called myelin, is damaged by a variety of so called “demyelinating diseases,’ the most common of which is multiple...
by | | Research
Who knew that a product of sadness could be so beautiful? There are three different types of human tears: basal (which keep the eyes wet), reflex (which occur with eye irritation), and emotional (which spring up with strong feelings). Each type has a distinct chemical...
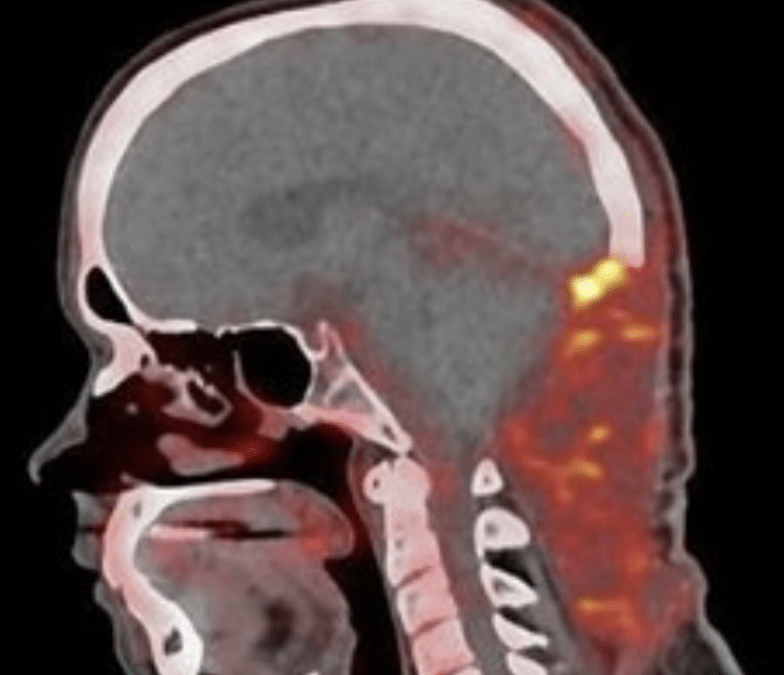
by | | Research
Humans aren’t the only organisms with a sweet tooth, bacteria love sweets too. With a new medical imaging technique developed by pediatrician Alvaro Ordonez and a team of researchers, PET scans can capture images of infection-causing bacteria in the human body with...

by | | Research
A new study shows that teen at risk for adult obesity have less active self-regulation system in the brain. In a small study that scanned the brains of teenagers while exposing them to tempting “food cues,” researchers report that reduced activity in the brain’s... 







Recent Comments